title: Animal Image Classification Using InceptionV3
emoji: 🐍
colorFrom: blue
colorTo: red
sdk: gradio
sdk_version: 6.5.1
app_file: app.py
pinned: false
license: mit
short_description: InceptionV3-based animal image classifier with data cleaning
models:
- AIOmarRehan/Animal-Image-Classification-Using-CNN
datasets:
- AIOmarRehan/AnimalsDataset
If you would like a detailed explanation of this project, please refer to the Medium article below.
Animal Image Classification Using InceptionV3
A complete end-to-end pipeline for building a clean, reliable deep-learning classifier.
This project implements a full deep-learning workflow for classifying animal images using TensorFlow + InceptionV3, with a major focus on dataset validation and cleaning. Before training the model, I built a comprehensive system to detect corrupted images, duplicates, brightness/contrast issues, mislabeled samples, and resolution outliers.
This repository contains the full pipeline—from dataset extraction to evaluation and model saving.
Features
Full Dataset Validation
The project includes automated checks for:
- Corrupted or unreadable images
- Hash-based duplicate detection
- Duplicate filenames
- Misplaced or incorrectly labeled images
- File naming inconsistencies
- Extremely dark/bright images
- Very low-contrast (blank) images
- Outlier resolutions
Preprocessing & Augmentation
- Resize to 256×256
- Normalization
- Light augmentation (probabilistic)
- Efficient
tf.datapipeline with caching, shuffling, prefetching
Transfer Learning with InceptionV3
- Pretrained ImageNet weights
- Frozen base model
- Custom classification head (GAP → Dense → Dropout → Softmax)
- EarlyStopping + ModelCheckpoint + ReduceLROnPlateau callbacks
Clean & Reproducible Training
- 80% training
- 10% validation
- 10% test
- High stability due to dataset cleaning
1. Dataset Extraction
The dataset is stored as a ZIP file (Google Drive). After mounting the drive, it is extracted and indexed into a Pandas DataFrame:
drive.mount('/content/drive')
zip_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/Animals.zip'
extract_to = '/content/my_data'
with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_path, 'r') as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall(extract_to)
Each image entry records:
- Class
- Filename
- Full path
2. Dataset Exploration
Before any training, I analyzed:
- Class distribution
- Image dimensions
- Grayscale vs RGB
- Unique sizes
- Folder structures
Example class-count visualization:
plt.figure(figsize=(32, 16))
class_count.plot(kind='bar')
This revealed imbalance and inconsistent image sizes early.
3. Visual Sanity Checks
Random images were displayed with their brightness, contrast, and shape to manually confirm dataset quality.
This step prevents hidden issues—especially in community-created or scraped datasets.
4. Data Quality Detection
The system checks for:
Duplicate Images (Using MD5 Hashing)
def get_hash(path):
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return hashlib.md5(f.read()).hexdigest()
df['file_hash'] = df['full_path'].apply(get_hash)
duplicate_hashes = df[df.duplicated('file_hash', keep=False)]
Corrupted Files
try:
with Image.open(file_path) as img:
img.verify()
except:
corrupted_files.append(file_path)
Brightness/Contrast Outliers
Using PIL’s ImageStat to detect very dark/bright samples.
Label Consistency Check
folder = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(row["full_path"]))
This catches mislabeled entries where folder name ≠ actual class.
5. Preprocessing Pipeline
Custom preprocessing:
- Resize → Normalize
- Optional augmentation
- Efficient
tf.databatching
def preprocess_image(path, target_size=(256, 256), augment=True):
img = tf.image.decode_image(...)
img = tf.image.resize(img, target_size)
img = img / 255.0
Split structure:
| Split | Percent |
|---|---|
| Train | 80% |
| Validation | 10% |
| Test | 10% |
6. Model — Transfer Learning with InceptionV3
The model is built using InceptionV3 pretrained on ImageNet as a feature extractor.
inception = InceptionV3(
input_shape=input_shape,
weights="imagenet",
include_top=False
)
At first, all backbone layers are frozen to preserve pretrained representations:
for layer in inception.layers:
layer.trainable = False
A custom classification head is added:
- GlobalAveragePooling2D
- Dense(512, ReLU)
- Dropout(0.5)
- Dense(N, Softmax) — where N = number of classes
This setup allows the model to learn dataset-specific patterns while avoiding overfitting during early training.
7. Initial Training (Frozen Backbone "Feature Extraction")
The model is compiled using:
- Loss:
sparse_categorical_crossentropy - Optimizer: Adam
- Metric: Accuracy
Training is performed with callbacks to improve stability:
- EarlyStopping (restore best weights)
- ModelCheckpoint (save best model)
- ReduceLROnPlateau
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
validation_data=val_ds,
epochs=5,
callbacks=callbacks
)
This stage allows the new classification head to converge while keeping the pretrained backbone intact.
8. Fine-Tuning the InceptionV3 Backbone
After the initial convergence, fine-tuning is applied to improve performance.
The last 30 layers of InceptionV3 are unfrozen:
The model is then recompiled and trained again:
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
validation_data=val_ds,
epochs=10,
callbacks=callbacks
)
Fine-tuning allows higher-level convolutional filters to adapt to the animal dataset, resulting in better class separation and generalization.
9. Model Evaluation
The final model is evaluated on a held-out test set.
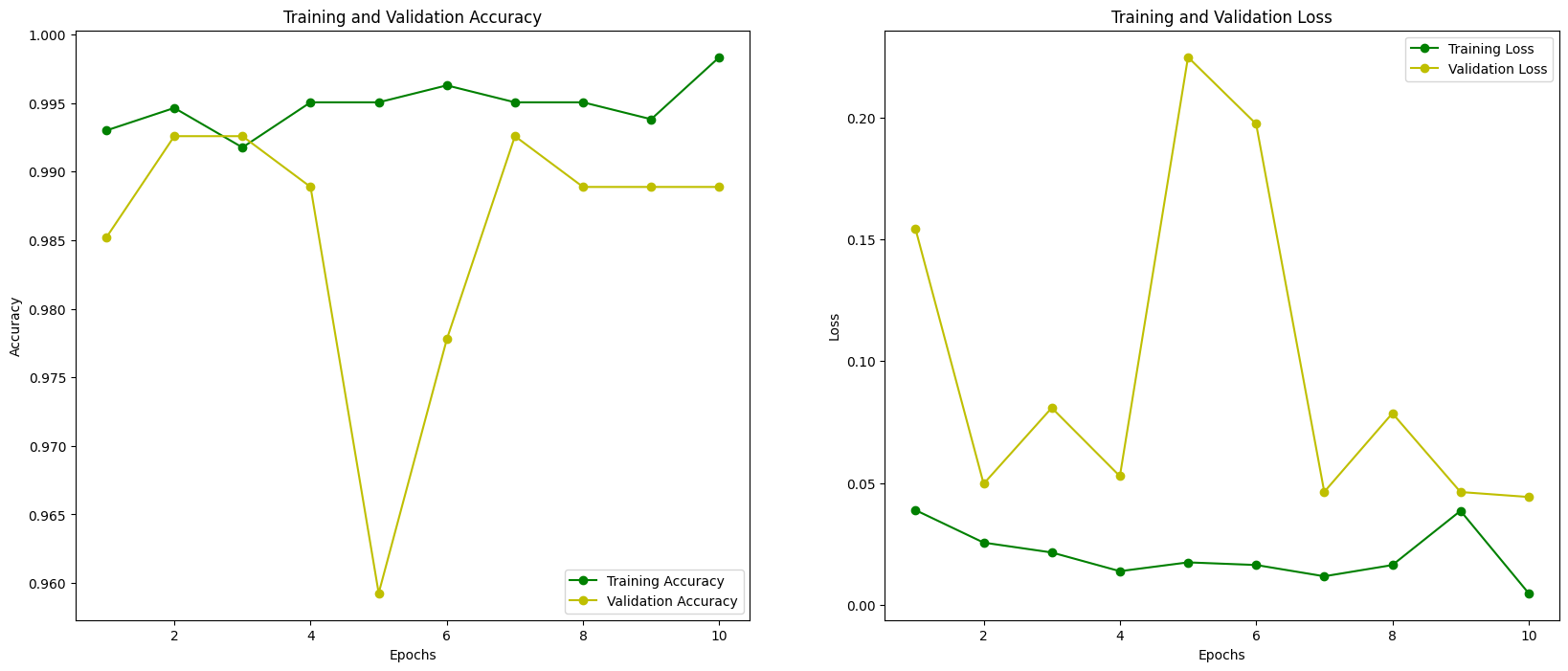
Accuracy & Loss Curves
Training and validation curves are plotted to monitor:
- Convergence behavior
- Overfitting
- Generalization stability
These plots confirm that fine-tuning improves validation performance without introducing instability.
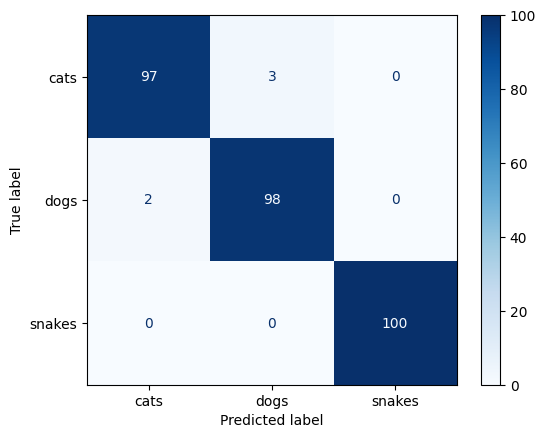
Confusion Matrix
A confusion matrix is computed to visualize class-level performance:
- Highlights misclassification patterns
- Reveals class confusion (e.g., visually similar animals)
Both annotated and heatmap-style confusion matrices are generated.
Classification Metrics
The following metrics are computed on the test set:
- Accuracy
- Precision (macro)
- Recall (macro)
- F1-score (macro)
A detailed per-class classification report is also produced:
- Precision
- Recall
- F1-score
- Support
This provides a deeper understanding beyond accuracy alone.
10/10 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 106ms/step - accuracy: 0.9826 - loss: 0.3082 - Test Accuracy: 0.9900
10/10 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 93ms/step
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
cats 0.99 0.97 0.98 100
dogs 0.97 0.99 0.98 100
snakes 1.00 1.00 1.00 100
accuracy 0.99 300
macro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 300
weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 300
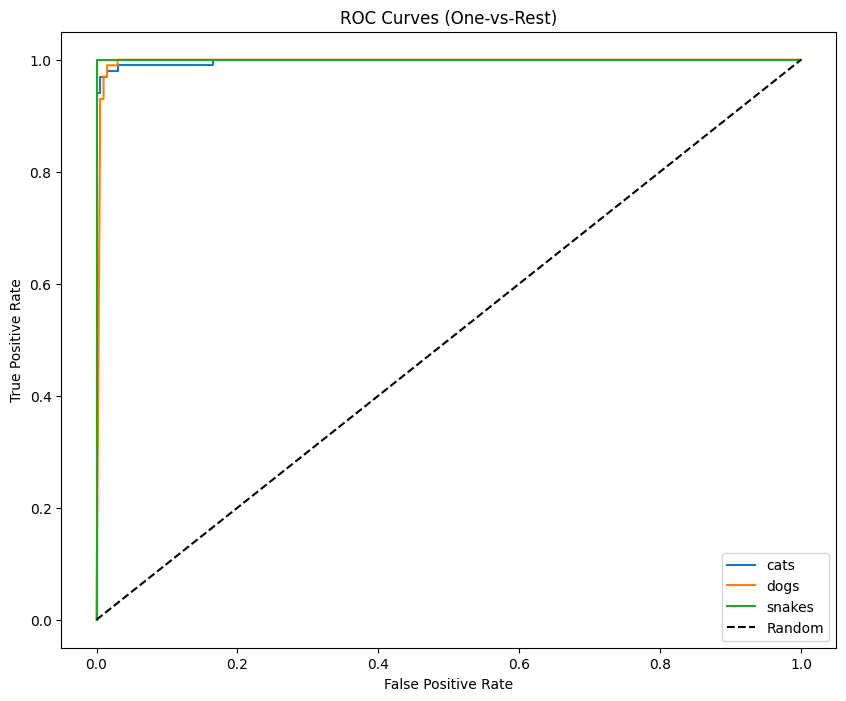
ROC Curves (Multi-Class)
To further evaluate model discrimination:
- One-vs-Rest ROC curves are generated per class
- A macro-average ROC curve is computed
- AUC is reported for overall performance
These curves demonstrate strong separability across all classes.
10. Final Model
The best-performing model (after fine-tuning) is saved and later used for deployment:
model.save("Inception_V3_Animals_Classification.h5")
This trained model is deployed using FastAPI + Docker for inference and Gradio on Hugging Face Spaces for public interaction.
Updated Key Takeaways
Clean data enables strong fine-tuning.
By combining:
- Rigorous dataset validation
- Transfer learning
- Selective fine-tuning
- Comprehensive evaluation
the model achieves high accuracy, stable convergence, and reliable real-world performance.
Fine-tuning only a subset of pretrained layers strikes the optimal balance between generalization and specialization.